This site uses only a few technical cookies necessary for its operation. By continuing to browse, you accept their use.
To find out more...
To find out more...
What happens to the bread when you make it?

This bread that we eat every day, and that our baker makes for us, what happens during its manufacture so that it becomes bread?
I will try to answer this question, and to summarize the complex alchemy that takes place.
I will try to answer this question, and to summarize the complex alchemy that takes place.
15 K 4.9/5 (19 reviews)
Last modified on: May 28th 2021
What happens to the bread when you make it?
What's in bread?
Let's start with the basics, for classic bread, which is improperly called "white bread", baguette for example, it's extremely simple there can/should only be 4 things: flour, water, a bit of salt, and a dollop of yeast or leaven, or sometimes both. Full stop!All the rest: additives, improvers, flavour enhancers, correctors, etc. are chemicals, "crutches" as the bakers say, additions that are only there for bad bakers or the food industry, or both, and that have no place in a good quality bread.
I'll detail a bit: Flour contains mainly starch (a sugar), a lot, and gluten (a protein), quite a bit.
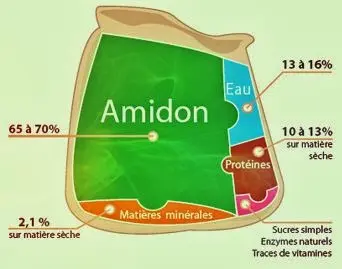
What happens?
As soon as the baker mixes the water, flour, and yeast/leaven, it starts, a complex mechanism gets underway, which will result in the little daily miracle of crusty bread.1) On the first hand, the yeast or sourdough, microscopic fungi, will attack the starch, and produce carbon dioxide, CO2 and alcohol.
This is the so-called alcoholic fermentation, the same as in wine and beer, but don't worry about the alcohol, it will disappear when cooked (at 250°C).
2) On the other hand, kneading the future dough acts mechanically on its gluten, little by little this protein structures itself into a network, and thus forms a rather elastic dough, which is at the same time capable of retaining the CO2 produced by the fermentation.
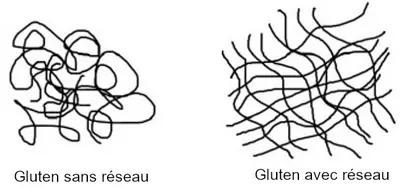
It is this CO2, trapped by the network, which cannot escape and which forms bubbles in the dough, bubbles which will become cells in the bread once it is baked.
The dough is said to be structured or "networked" when the kneading is finished, a moment not so easy to determine.

You see it's a duo of action, one without the other, would not give good bread :
- No fermentation => no CO2 => flat, hard dough => inedible bread.
- No gluten network => the CO2 from the fermentation escapes because it is not retained => flat and hard dough => bread that is also inedible.
The dough, well kneaded and leavened, is put in the oven, at around 250°C, the alcohol is quickly eliminated, the cooking at the beginning accelerates a little the production of CO2 from the yeast, the dough still rises, then the cooking really starts and freezes everything.
The bubbles are cooked, the crumb is aerated, and the crust turns golden under the action of the famous Maillard reactions.
And in the end, a crisp, golden bread with a delicious smell spreads all around the oven.

Is that all?
Well in broad strokes yes, overall it's all there, but it's the whole difficulty of the baking trade to manage these 2 aspects of fermentation and kneading, then baking, to make you, regularly, a good loaf.Some points of detail
- The gluten network, this is what makes a gluten-free bread very difficult to make, it's not really bread some would say, it's impossible others would say, because you have to manage to imitate a network to trap the CO2, either by adding a binder (bof!) or by moulding the dough, a bit like a cake, or both. This is why gluten-free breads look more like cakes than breads.It should also be noted that the gluten of today is very different from that of just 50 years ago, the original sin coming from the 70's when we started to make bread, faster and faster, whiter and whiter and more and more bland, and therefore increased the gluten content of the flours, and also selected short-legged wheats, richer and richer in an increasingly strong gluten. This is undoubtedly the main cause of the many gluten-related problems of our time, a gluten that is much less digestible than before.
One last piece of information about gluten, sourdough breads, apart from their extraordinary taste and nutritional advantages, and partly thanks to their long, even very long, fermentation times, these sourdough breads therefore favour the digestibility of gluten.
In other words, if you have problems with gluten in your daily diet, try (quality) sourdough bread.
- The fermentation-kneading duo does not only apply to bread, but also to viennoiserie (brioche, croissants,...) to pizzas, and in fact to all the so-called "fermented" doughs precisely, it's the borderline between baking and pastry-making.
Respectus panis
If you don't knead the dough, no gluten network you will have understood, but there is another alternative which is time: If you only mix the ingredients, 1 or 2 minutes maximum, and leave the dough for a very long time (18 to 20 hours) at around 16°C with very little yeast/leaven and less salt, the network will still build up by itself, very slowly, but surely. "Time is on my side", if you have the Stones ref...
In summary: Bread is a duo of actions, kneading (1) to form the gluten network, which will trap the CO2 from fermentation (2).
Lasts posts
XO Cognac Explained: Meaning, Aging, and Flavor Profile
XO Cognac always goes beyond the labels on the bottle: it is often associated with tradition and quality. You get to appreciate the artistry, character and ageing process when you understand what defines this smooth Cognac. The section below tackles everything about XO Cognac, from complex flavour...January 28th 20261,061 Sponsored article
Butter vs. grease
We often read in a recipe where a pastry is put into a mould that, just before pouring, the mould should be buttered or greased. But what's the difference between these 2 terms?December 1st 20252,6605
Getting out of the fridge early
Very often when you're cooking, you need to take food or preparations out of the fridge, to use them in the recipe in progress. There's nothing tricky about this: you just take them out of the fridge and use them, usually immediately, in the recipe. But is this really a good method?November 24th 20251,7035
Who's making the croissants?
When you look at a bakery from the outside, you naturally think that in the bakery, the bakers make the bread, and in the laboratory, the pastry chefs make the cakes. It's very often like that, with each of these professions having quite different ways of working, but sometimes there's also one...November 23th 20251,559
Oven height
When we put a dish or cake in the oven, we naturally tend to put it on the middle shelf, and that's what we usually do. But in some cases, this position and height can be a little tricky, so let's find out why.October 8th 20255,2795
Other pages you may also like
What is the difference between bakery and patisserie?
This is a question that you may well have asked yourself and which I will attempt to answer. In France the two trades of "boulangerie" (bakery) and "pâtisserie" (patisserie and confectionery) have always been quite distinct, but where exactly do the boundaries lie? .February 7th 2017135 K 14.1
Candied fruits: don't get ripped off
Do you like candied fruit? You might like to nibble a handful or add it to a recipe, like a classic fruit cake or delicious Italian specialities like panettone or sicilian epiphany pie.June 21th 201769 K 24.2
The bitterness of endives
As I write these lines, we are entering the endive season, and if you like it, it's time to enjoy it, if possible with your local producers. Endive is good, but the reproach that is often made of it, and children in particular, is: "It's bitter! And it is (somewhat) true of course, endives...February 9th 201915 K4.9
How to zest a fruit?
You will have no doubt noticed that many recipes call for the zest of citrus fruit. The zest is that outer layer of the skin which adds so much flavour to a dish. There are many different ways to peel off the zest and various tools are available. Here is a summary of the “dos and don'ts” of...November 5th 201348 K3.8
Perpetual stock
It's something you have probably have done yourself: cooked or pre-cooked vegetables before adding them to a recipe. This is almost always done the same way: peel the chosen vegetables (carrots, for example), cut them up, boil them in salted water (using a tablespoon or so of coarse salt per litre),...November 22th 201632 K5
Post a comment or question
Follow this page
If you are interested in this page, you can "follow" it, by entering your email address here. You will then receive a notification immediately each time the page is modified or a new comment is added. Please note that you will need to confirm this following.
Note: We'll never share your e-mail address with anyone else.
Alternatively: you can subscribe to the mailing list of cooling-ez.com , you will receive a e-mail for each new recipe published on the site.









